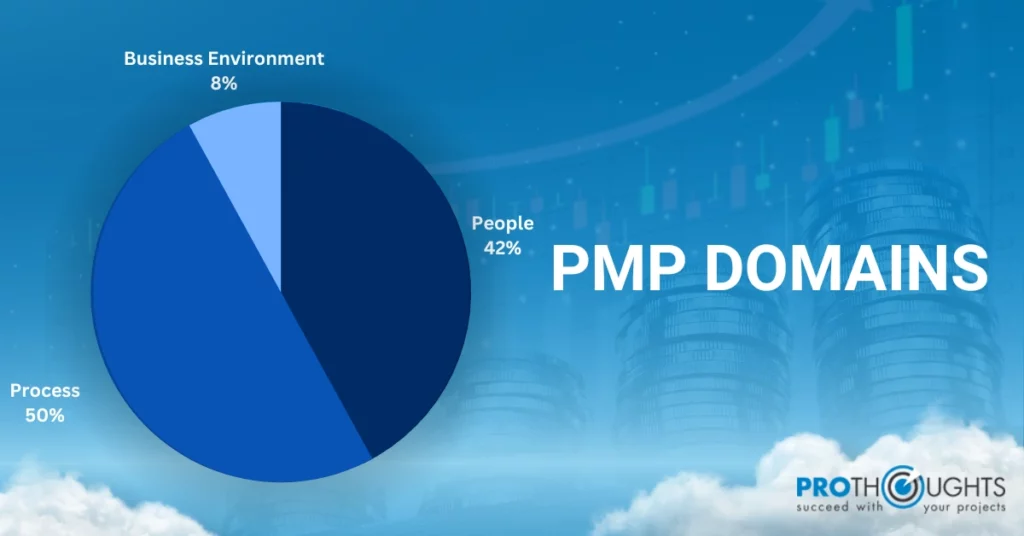
Welcome to the world of PMP domains, where success in project management comes to life. These domains – People, Process, and Business Environment – serve as your navigational stars, guiding you through the complexities of project execution.
Whether you’re a PMP candidate aiming to ace the certification or a seasoned project manager seeking to sharpen your skills, this guide is your trusted companion. Our goal is to provide you with practical insights and strategies that will assist you in excelling in project management.
Are you ready to unlock the power of PMP domains and become a successful project manager? Let’s dive in and embark on this transformative adventure together!
Introduction to the PMP Certification
PMP certification is a globally recognized certification offered by the (PMI). It signifies a high level of expertise and proficiency in project management. PMP certification validates the skills and knowledge required to successfully lead and manage projects, ensuring they are completed within time, scope, and within budget.
Importance of Understanding the Three PMP Domains within the Framework
The framework for the certification is structured around three PMP domains encompassing various project management aspects. Moreover, these PMP domains are crucial for effective project management as they provide a comprehensive framework to address project managers’ diverse challenges and responsibilities.
How do These PMP Domains Contribute to Effective Project Management?
1. People
The People domain of PMP emphasizes the human side of project management. It involves understanding and managing interpersonal relationships, leadership, team dynamics, and stakeholder engagement. Furthermore, effective communication, motivation, and conflict resolution within the project team create a positive and productive work environment, which results in improved team morale.
2. Process
Process management is at the core of project execution. It covers the technical aspects of project management, such as project planning, execution, monitoring, controlling, and closing. A solid grasp process ensures that projects are well-structured, tasks are well-defined, risks are managed, and quality standards are met. Therefore, a well-established process promotes consistency, reduces errors, and increases the chance of success.
3. Business Environment
This domain focuses on the broader organizational context in which projects operate. It involves understanding the strategic alignment of projects with corporate goals, considering regulatory and legal factors, and managing external influences such as market conditions and industry trends. Furthermore, project managers who comprehend the business environment can make informed decisions that optimize project outcomes in line with the organization’s overall strategy.
What Do PMP Domains Represent?
In the context of the Project Management Professional (PMP) certification, PMP domains represent overarching knowledge and expertise that project managers must possess to manage projects effectively. Moreover, these PMP domains provide a structured framework for categorizing and organizing the various knowledge areas and competencies essential for successful project execution. Also, each domain encompasses a distinct set of skills, activities, and responsibilities that collectively contribute to proficient project management.
The PMP certification training that you undergo teaches you how exactly you can apply these PMP domains most effectively. Enroll now and elevate your career with PMP certification online training.
How Do Domains Categorize and Organize Project Management Knowledge Areas?
PMP Domains serve as a higher-level classification system that groups related topics within project management knowledge areas. Knowledge areas are specific facets of project management that address distinct aspects of project planning, execution, monitoring, and control. The domains, therefore, offer a way to organize these knowledge areas into broader categories, creating a holistic approach to project management.
Firstly, the “People” domain covers knowledge areas such as team management, leadership, and stakeholder engagement. Secondly, The “Process” domain encompasses project planning, risk management, and quality control. Lastly, the “Business Environment” domain includes knowledge of organizational strategy, compliance, and external factors impacting projects. Therefore, by categorizing knowledge areas into parts, the PMP framework provides a structured and systematic approach to understanding and applying project management concepts.
Role of PMP Domains
Project management domains are a framework for categorizing, organizing, and addressing all the knowledge areas and competencies needed to manage a project effectively. These PMP domains play a crucial role in guiding project managers through the complexities of project execution and ensuring that all critical aspects are considered. The following is a closer look at the parts of PMP domains:
-
Structural Framework
PMP domains establish a clear and organized structure that groups related knowledge areas together. Moreover, its design simplifies the understanding of project management concepts by creating distinct categories covering different aspects of project execution, from team management to risk assessment.
-
Focused Guidance
Each PMP domain offers focused guidance on specific areas of project management. Therefore, this guidance helps project managers develop a deeper understanding of critical concepts, techniques, and best practices associated with each domain, enabling them to make informed decisions and take appropriate actions.
-
Comprehensive Coverage
By categorizing knowledge areas within PMP domains, the framework ensures comprehensive coverage of all essential aspects of project management. Moreover, a comprehensive approach equips project managers with a well-rounded skill set to handle various challenges, opportunities, and risks that may arise during project implementation.
-
Effective Communication
PMP domains facilitate effective communication among project managers, team members, and stakeholders. The standardized terminology and categorization provided by fields enable clear and concise communication, fostering collaboration and understanding among project professionals.
-
Strategic Alignment
PMP Domains contribute to strategic alignment by emphasizing the importance of considering the broader business context. In particular, the “Business Environment” domain encourages project managers to align projects with the overarching goals and strategies of the organization, thus contributing to the company’s success.
-
Tailored Approach
PMP domains allow project managers to tailor their approach based on each project’s specific requirements and characteristics. Understanding which domain(s) are most relevant to a particular project. Also, project managers can focus their efforts on the areas that will impact project success most.
-
Adaptability
The flexibility of PMP domains enables their application across diverse industries, project types, and organizational contexts. Project managers can adapt the principles and practices from each field to suit their projects’ unique needs and challenges.
-
Professional Development
The structured PMP domains provide a clear path for professional development in project management. As project managers gain expertise in each field, they enhance their competency and become better equipped to lead projects effectively.
In summary, domains in the PMP context represent overarching categories that organize and categorize the diverse knowledge areas and competencies required for successful project management. Also, they provide structure, guidance, and a comprehensive approach that enables project managers to navigate complexities, lead teams, and deliver successful projects.
Importance of PMP Domains in guiding Project Managers through various aspects of a Project
PMP Domains play a crucial role in guiding project managers through the multifaceted aspects of a project. They provide a structured framework that covers the diverse knowledge areas and competencies required for successful project management. Additionally, by focusing on specific domains, project managers can effectively navigate challenges, make informed decisions, and lead projects to successful outcomes. Furthermore, PMP domains offer a comprehensive approach that ensures project managers address people-related, process-oriented, and business-context factors, contributing to a well-rounded and holistic project management approach.
How do the Domains align with the Project Management Process?
The PMP domains align with the project management process by providing a logical sequence of activities and considerations that project managers should follow throughout the project lifecycle. As a result, the domains correspond to different phases of the project management process, guiding project managers throughout the project lifecycle. By understanding and applying the principles within each field, project managers can seamlessly navigate the various PMP process while considering the aspects of people, processes, and business environment.
The Three PMP Domains
Domain #1 People
People Management
1. Importance of Effective Communication and Leadership – Clear and open communication is essential for conveying project objectives, expectations, and changes. Moreover, effective leadership ensures that the project team is aligned, motivated, and empowered to deliver their best performance.
2. Building and Nurturing High-Performing Project Teams – Successful project outcomes depend on cohesive and skilled teams. Therefore, project managers must focus on team member strengths, provide support, and create an environment conducive to collaboration and growth.
Team Dynamics
1. Managing Conflicts and Promoting Collaboration – Conflicts are inevitable, but effective project managers address them promptly and promote collaboration to maintain a positive team dynamic and productive work atmosphere.
2. Motivating and Engaging Team Members – Motivated team members are likelier to be engaged and contribute their best efforts. Moreover, project managers must understand individual motivations and provide opportunities for professional growth and recognition.
PMP Domain #2: Process
Project Lifecycle and Approach
1. Understanding Project Phases and Methodologies – Different projects require different approaches. Therefore, project managers should have a grasp of various project methodologies and select the most suitable one for each project.
2. Selecting and Tailoring Appropriate Project Approaches – The right project approach ensures efficient resource allocation, risk management, and alignment with project goals and constraints. The tailored approach ensures projects succeed faster and more effectively.
Planning and Strategy
1. Developing Comprehensive Project Plans and Defining Scope – A well-defined project plan outlines tasks, milestones, and deliverables, ensuring everyone is on the same page. Also, defining scope helps prevent scope creep and provides project focus.
2. Identifying and Managing Project Risks – Effective risk management involves identifying potential issues and developing strategies to mitigate them, enhancing the project’s chances of success.
PMP Domain #3: Business Environment
Business and Organization Context
The “Business Environment” domain focuses on the broader organizational context in which projects operate.
1. Recognizing Different Organizational Structures and Their Impact on Projects – Different organizations have varying structures, such as functional, matrix, or projected. Understanding these structures helps project managers navigate communication channels, decision-making processes, and resource allocation. As a result, there is effective collaboration and integration.
2. Aligning Project Objectives with Business Goals and Strategies – Project success is closely tied to its alignment with the overall business goals and strategies. Project managers must ensure that their projects contribute to the organization’s long-term vision, mission, and strategic objectives, maximizing their value and relevance.
Regulatory and Ethical Considerations
1. Navigating the Complex Terrain of Regulatory Compliance – Complying with regulatory mandates requires constant vigilance, awareness, and proactive measures. Additionally, project managers provide precision and dedication as navigators through this complex terrain.
2. Stressing the Significance of Addressing Ethical Considerations – Ethics in project management is the pattern that guides decision-making, actions, and interactions. Also, addressing ethical considerations is not a secondary pursuit; it is a primary commitment that shapes project credibility and the perception of project managers as stewards of integrity.
Highlighting the Interconnectedness of the Three Domains
The three Project management domains are a complex weave of PMP skills, not distinct stores. Understanding the complexity of project success is similar to comprehending how they are interconnected. Additionally, decisions taken in one area always impact others, resulting in a triumphant project management symphony.
How Do Decisions Made in One Domain Influence The Others?
Decisions within a specific domain have a cascading effect on the entire project ecosystem. A prime example is the relationship between “People Management” and “Process.” A harmonious team dynamic (People Management) can catalyze smoother project execution (Process). Conversely, a meticulously planned project approach (Process) can provide clarity and motivation to the project team (People Management). This delicate interplay showcases how the domains are not stand-alone entities but interconnected gears that drive project progress.
Case Study: Applying Domains in Harmony
1. Real-world Examples Illustrating Practical Application – Picture a construction project where the Project Manager (People) effectively communicates project goals and motivates the team. Furthermore, the team strategically plans phases and allocates resources (Process), aligning each step with the organization’s business goals (Business Environment). Therefore, the PMP application showcases how proficiency across domains leads to successful project outcomes.
2. Demonstrating a Balanced Approach Across Domains – A software development project highlights the synergy between domains in another scenario. The team’s cohesive collaboration (People) ensures efficient development processes (Process), while the project’s alignment with the organization’s technological strategy (Business Environment) contributes to its overall success.
Conclusion
As we draw the threads of this guide together, it becomes evident that mastering the three Project management domains is pivotal for holistic project management. Moreover, each domain’s unique contributions combine to create a comprehensive skill set indispensable for successful project execution. The fields represent more than study segments for those embarking on the PMP journey. They are keys to unlocking project excellence. Therefore, by mastering these PMP domains, you equip yourself to lead projects with confidence, insight, and strategic finesse.
